Profit maximization of the farmer:
Natural farming is a normal business of the farmer for earning their
livelihood therefore, the ultimate goal of natural farming is their profit maximisation. The
factors that contribute to the profit maximisation of farmers are
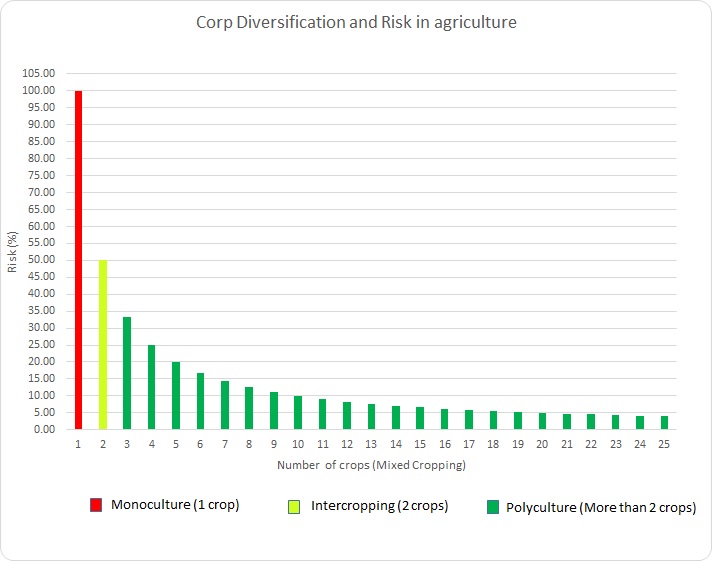
(1) Minimum risk -agriculture
is practised in the open field therefore it faces different kinds of risks such as climate risk
(low or high temperature, low or high rainfall, high wind, hailstorm, lightning), biotic risk
(outbreak of insect pests, diseases, weeds and wild animals) and market risk (low demand, over
supply, low price). Crop diversification in polyculture can reduce risk and increase returns in
agriculture.
(2) Minimum cost of production - natural farming completely depends on natural
capital and ecosystem services for crop production and crop protection. The farmers need not
purchase any input from the market, hire any machine or labour for carrying out natural farming,
which saves huge cost.
(3) Maximum crop yield - the aggregate crop production per year is
highest in natural farming. Application of advanced methods such as selection of the best
varieties, optimization of crop portfolio, and optimization of landscape design to maximise the
leaf area index can maximise the aggregate crop yield,
(4) maximum product diversity - maximum
crop diversity, farm animal diversity and aquatic animal diversity effectively make natural
farming agroecosystem an agricultural supermarket with diversified product range.
(5) Maximum product quality - natural farming produces premium quality products through breeding of
exclusive and exquisite plant varieties, breeding exclusive animal breeds, selection of the best
plant varieties, selection of off-season or all-season varieties, elimination of chemical
fertilisers, growth regulators, pesticides and chemical fruit ripeners and biotic pollination of
crops by native pollinator biodiversity,
(6) Maximum price of crops - direct marketing of crops
gives complete liberty to the farmers to fix the price of their own crops and they tend to fix a
premium price for their premium products,
(7) Regular cash flow - crop diversification and use
of off-season or all-season varieties help mixed harvesting of multiple crops on a daily basis,
generating daily cash flow and passive income for the farmer,
(8) Law of increasing marginal returns -the income from the natural farming agroecosystems gradually increase over time but
the cost of production gradually decreases over time. As a result, income and profit increase
steadily.
(9) Sustainability of profit margin -continuous improvement of soil health, plant
health, animal health, human health and agro-ecosystem health increase sustainability in natural
farming agro-ecosystem.
(10) Resilience of the agro-ecosystem -natural farming depends on
biodiversity because biodiversity imparts resilience against abiotic, biotic and financial risks
in agriculture.
Conservation of natural resources:
Natural farming completely depends on natural capital (natural resources) and ecosystem services for crop production and crop protection. The recycling of natural resources (such as water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) in the natural farming agroecosystem ensures conservation of natural resources and gradual increase in natural wealth.
Conservation of biodiversity:
Natural farming depends on the biodiversity of organisms (plants, animals and microorganisms) to maximise its crop production and crop protection. Therefore natural farming agroecosystems intentionally restore and conserve biodiversity of organisms in the best possible way.
Nutritional security of the consumers:
Natural farming not only ensures food security of the nation but also ensures nutritional security of the consumers (including the farmers). Extreme crop diversification in natural farming agroecosystems ensure balanced nutrition of the farmers and consumers as well as the chemical-free farming provides the best of health and immunity against diseases. Farmers no longer need to buy any food ingredient from the market.
Restoring Natural Justice for the Farmers:
Natural farming ensures complete freedom of the farmers to acquire agricultural knowledge from tradition and personal experiences, to breed their own exclusive and exquisite plant varieties, to maintain and exchange their seeds, to innovate their unique methods of agriculture, to fix the price of their crops, to sell their crops directly to the consumers and to earn as much income from agriculture as they desire.